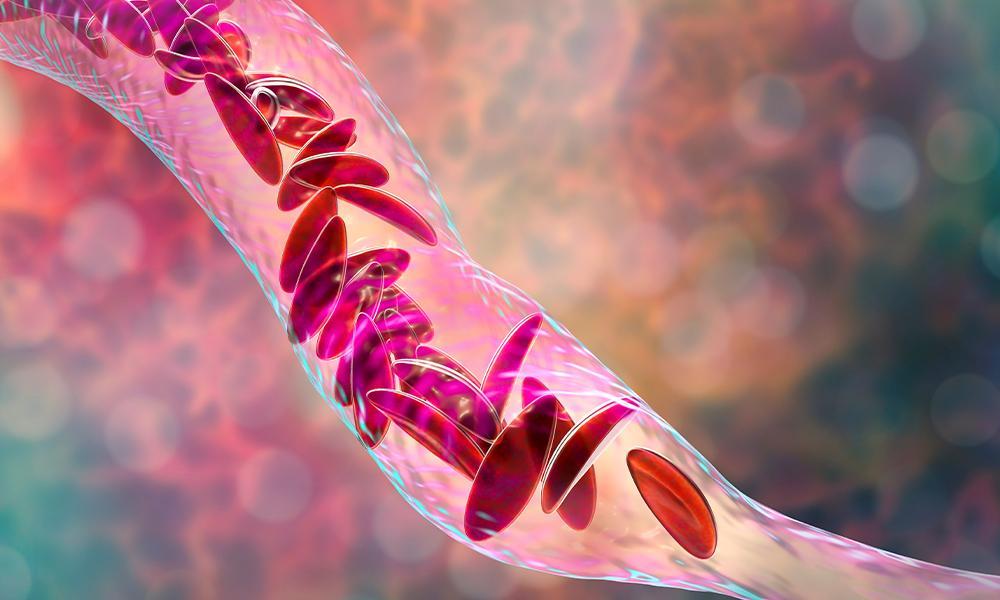
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a group of inherited blood disorders that affect millions of people worldwide, primarily those of African, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and Indian descent. It is characterized by abnormally shaped red blood cells, which can cause a range of health complications. In this blog post, we will explore the current treatments and ongoing research efforts in the field of Sickle Cell Disease, aimed at improving the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Understanding Sickle Cell Disease:
Sickle Cell Disease is caused by a mutation in the gene responsible for hemoglobin production, resulting in the production of abnormal hemoglobin called hemoglobin S. This abnormal hemoglobin causes red blood cells to become rigid, sticky, and take on a crescent or sickle shape. The sickle-shaped cells can block blood flow, leading to pain, organ damage, anemia, and various other complications.
Current Treatment Options:
Although there is no definitive cure for Sickle Cell Disease, several treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Pain management: Pain is one of the most common symptoms experienced by individuals with SCD. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, and other pain-relieving medications are used to alleviate pain during acute episodes, known as sickle cell crises.
- Hydroxyurea: Hydroxyurea is a medication that stimulates the production of fetal hemoglobin, which can help prevent sickle cell crises and reduce complications in some individuals with SCD. It has shown effectiveness in reducing the frequency of pain episodes and the need for blood transfusions.
- Blood transfusions: In severe cases of SCD, regular blood transfusions may be necessary to replace damaged red blood cells and improve oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues. Transfusions can help prevent complications and reduce the risk of stroke.
- Bone marrow transplantation: For a small number of individuals with severe SCD, a bone marrow transplant may be considered. This procedure involves replacing the diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor. It can potentially cure the disease but is associated with significant risks and is typically reserved for severe cases.
Ongoing Research and Promising Developments:
Researchers and medical professionals continue to explore new treatments and advancements in the field of Sickle Cell Disease. Some of the ongoing research efforts include:
- Gene therapy: Gene therapy holds promise as a potential cure for SCD. It involves modifying the patient’s own stem cells to produce healthy red blood cells and eliminate the production of sickle-shaped cells. Early studies have shown promising results, but more research is needed to ensure its long-term safety and effectiveness.
- New drug therapies: Several novel drug therapies are being investigated, including those that target specific molecules involved in the sickling process or promote the production of fetal hemoglobin. These therapies aim to reduce symptoms, decrease complications, and improve overall outcomes for individuals with SCD.
- Improved supportive care: Efforts are underway to enhance supportive care measures, including better pain management strategies, preventive measures for complications such as infections, improved access to healthcare services, and comprehensive psychological support.
- Global initiatives: International organizations, researchers, and policymakers are working together to increase awareness, improve diagnosis and treatment, and provide better support for individuals with SCD globally. These initiatives aim to reduce the burden of the disease, particularly in regions with limited resources.
Conclusion:
Sickle Cell Disease is a complex condition that requires ongoing management and care. While there is no cure currently available, treatment options such as pain management, hydroxyurea, blood transfusions, and bone marrow transplantation can help alleviate symptoms and reduce complications. Ongoing research and promising developments in gene therapy, new drug therapies, and improved supportive care provide hope for the future. It is crucial to support and invest in research initiatives, raise awareness, and advocate for better access to healthcare and support services for individuals with Sickle Cell Disease. With continued efforts, we can improve the lives of those living with this condition and work towards finding a cure.